From Ash to High-Performance Material
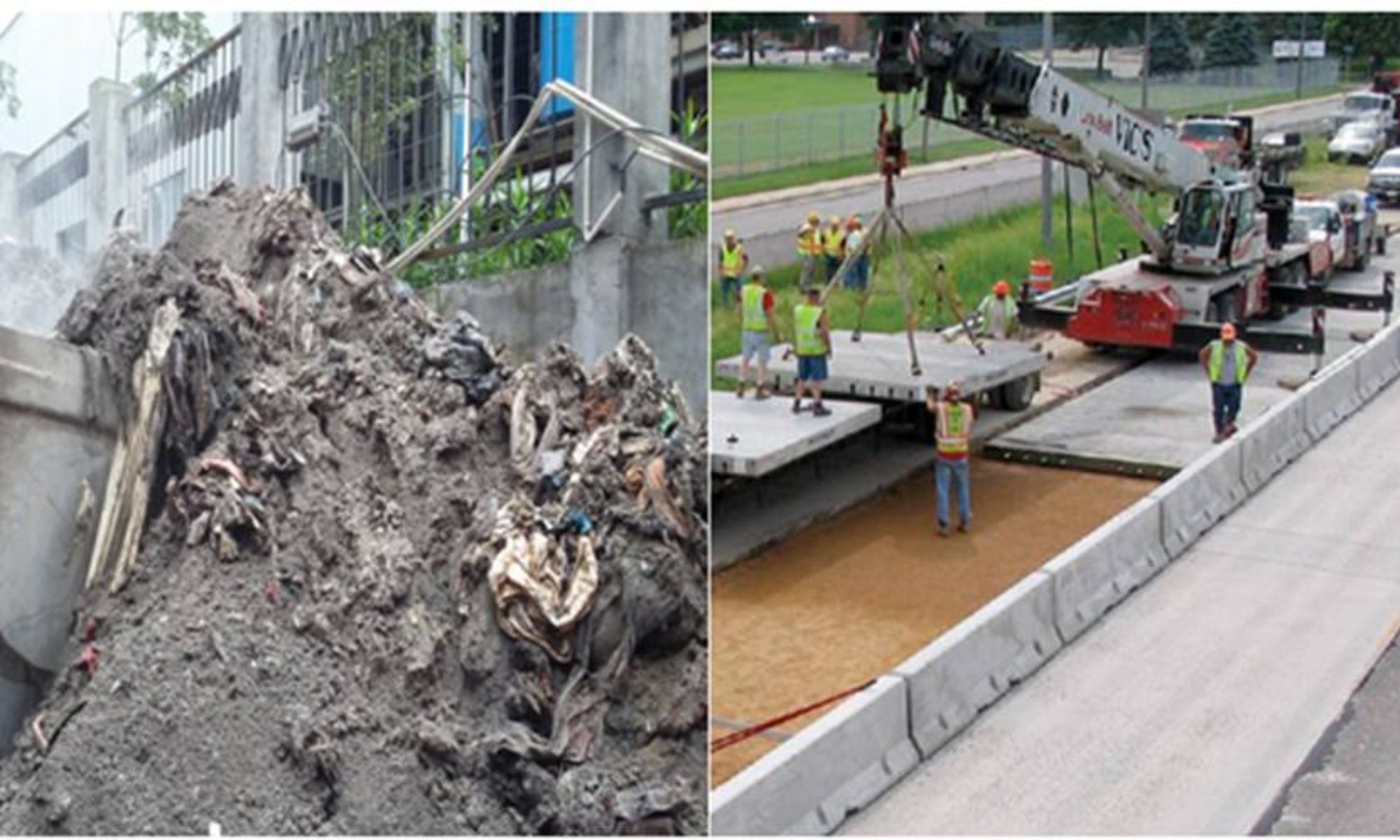
Ashcrete Technologies transforms freshly generated Waste-to-Energy (WTE) ash —typically a wet slurry—into a safe, high-performance material immediately after it exits the plant.
What We Do
- Instant Stabilization: Our proprietary process chemically binds moisture and fine particles on contact, eliminating leachate and dust emissions.
- Metal Recovery: Valuable ferrous and non-ferrous metals are extracted for reuse—advancing circular economy goals.
- Complete Transformation: Treated ash is combined with nano-composites and specialty binders to form a new engineered material that cures in under 24 hours. No ash remains—chemically or physically.
Why It Matters
- No leachate. No dust. No residual waste.
- No long-distance transport — system is mobile and scalable.
- No environmental liability — fully encapsulated, stable material.
- CO₂ capture potential — supports climate and waste goals.
Real-World Applications
Ashcrete’s transformed material can be used in:
Specialized Solutions: CO₂ mineralization, radiation shielding, emergency pads.
Civil Infrastructure: Road base, sidewalks, foundations, modular blocks, sound barriers.
Environmental Remediation: Sealing abandoned wells, riverbank stabilization, landfill capping.
Public Works: Bike paths, stormwater systems, flood barriers.
Industrial Uses: Rail underlay, warehouse floors, fireproof walls.

CO2 Capture and Permanent Storage
Globally, there are over 2,500 thermal Waste-to-Energy (WTE) plants, collectively emitting more than 280 million tons of CO₂ every year—a significant environmental challenge. But this global issue also opens the door to a transformative solution: by capturing and permanently storing CO₂ in the ash byproduct of incineration, the WTE sector can move toward carbon neutrality.
Our technology not only enables the secure storage of CO₂ within the ash, but also transforms the ash into Super Green Concrete—a high-performance material that eliminates the need for landfill disposal and continues to absorb CO₂ from other sources.
This innovation turns a major waste and emissions problem into a powerful climate solution—redefining Waste-to-Energy as a truly green technology and a vital engine of the circular economy worldwide.
Ash Ceases to Exist and Transform into a New Material Ash Ion Migration
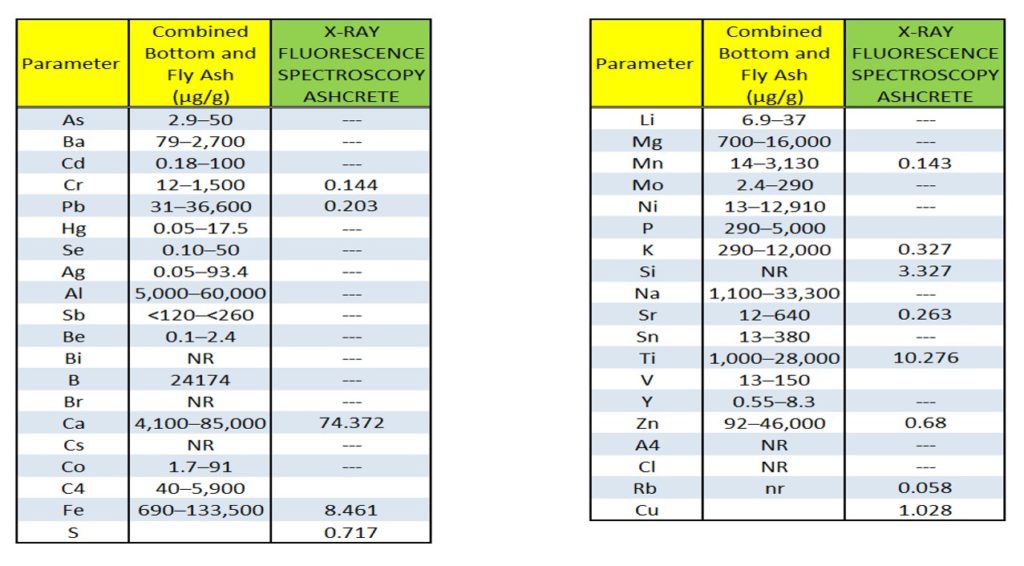
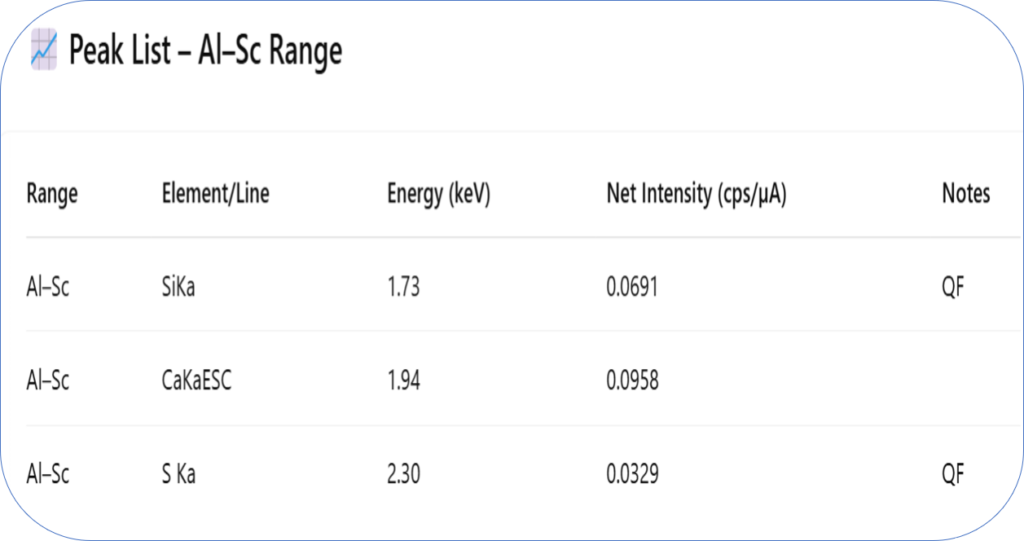
The below table shows the migration of elements, in yellow raw ash elements, in green XRF elemental analysis of Ashcrete (Composite concrete-like material made with MSW I. Ash).
Scientific Validation


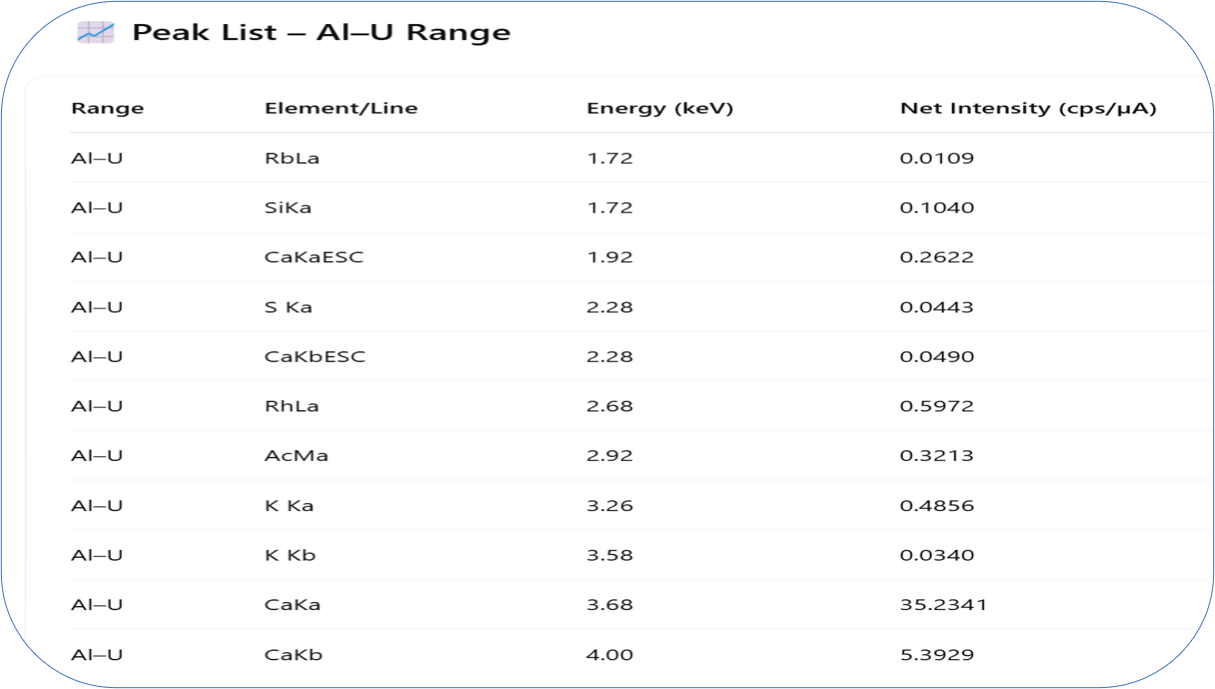
Scientific Validation Statement
This Ashcrete test confirms that ash has been chemically and structurally transformed into a new material. The final material no longer resembles incineration ash and is instead a high-performance cementitious product. Ash, as a waste material, ceases to exist.
This transformation is backed by elemental analysis and quantitative results that show the formation of new dominant phases. High calcium and iron content, along with minimized residual toxic elements, validate the stabilization and valorization process inherent in the Ashcrete technology.
The core of our innovation lies in a true material transformation—not just stabilization or encapsulation. Through our proprietary process, Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) ash—either Fly Ash, Bottom Ash, or Combined Ash—is subjected to a series of physicochemical treatments that alter its atomic structure and elemental composition, resulting in a new material with no resemblance, chemically or physically, to its original ash form.
How the Transformation Happens
- Chemical Activation and Acid Treatment: The ash undergoes a controlled acid treatment that breaks down unstable metal compounds, dissolves soluble phases, and initiates surface-level reactions. This disrupts the original matrix of the ash and allows us to selectively release and remove or convert hazardous components.
- Nanocomposite Integration and Rebuilding: Next, engineered nanocomposites and reactive agents are introduced. These materials interact with the liberated elements in the ash to form entirely new mineral phases—crystalline or amorphous—via chemical bonding. This step creates new compounds that are stable, non-leachable.
- Atomic-Level Rearrangement: Rather than trapping ash particles inside a binder (as in traditional stabilization or solidification), we rearrange atoms and reconstruct the material’s internal structure. Former ash-derived phases are replaced by silicate-based or geopolymer-like networks, depending on the ash type and input mix.
- Permanent Immobilization of Heavy Metals: Toxic elements such as Pb, Zn, Cd, and Cr are no longer free or loosely bonded. Instead, they are chemically bound within stable crystalline or glassy matrices, which prevent their leaching—even under extreme conditions.
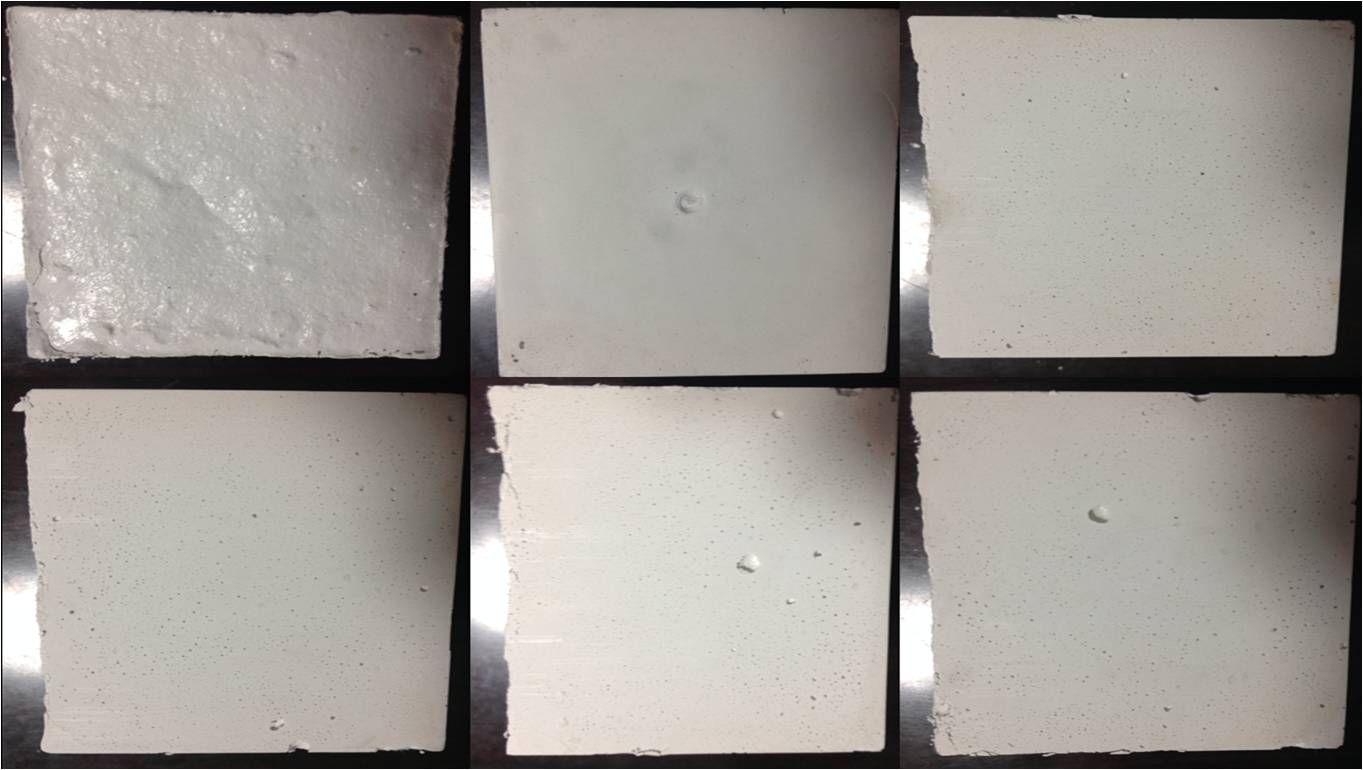
- Final Composite Formation (Ashcrete): The end product, Ashcrete, is chemically, structurally, and environmentally a new material. Its elemental fingerprint—as verified through X-ray fluorescence (XRF) testing—is significantly different from that of the untreated ash.
Evidence from XRF Testing
Raw Bottom Ash shows high levels of:
- Chlorides
- Sulfates
- Alkali metals (Na, K)
- Free lime (CaO)
- Heavy metals (Pb, Zn, Cu, etc.)
After treatment and transformation into Ashcrete, XRF tests reveal:
- A disappearance or major reduction in problematic elements (e.g., Cl, S, Pb, Zn).
- A new distribution of silicon, calcium, aluminum, and iron—indicating the formation of new silicate or aluminosilicate compounds.
- A completely different oxide profile—proving that the original ash is no longer present in its former chemical state.
TCLP Leaching Test
Key Scientific Findings
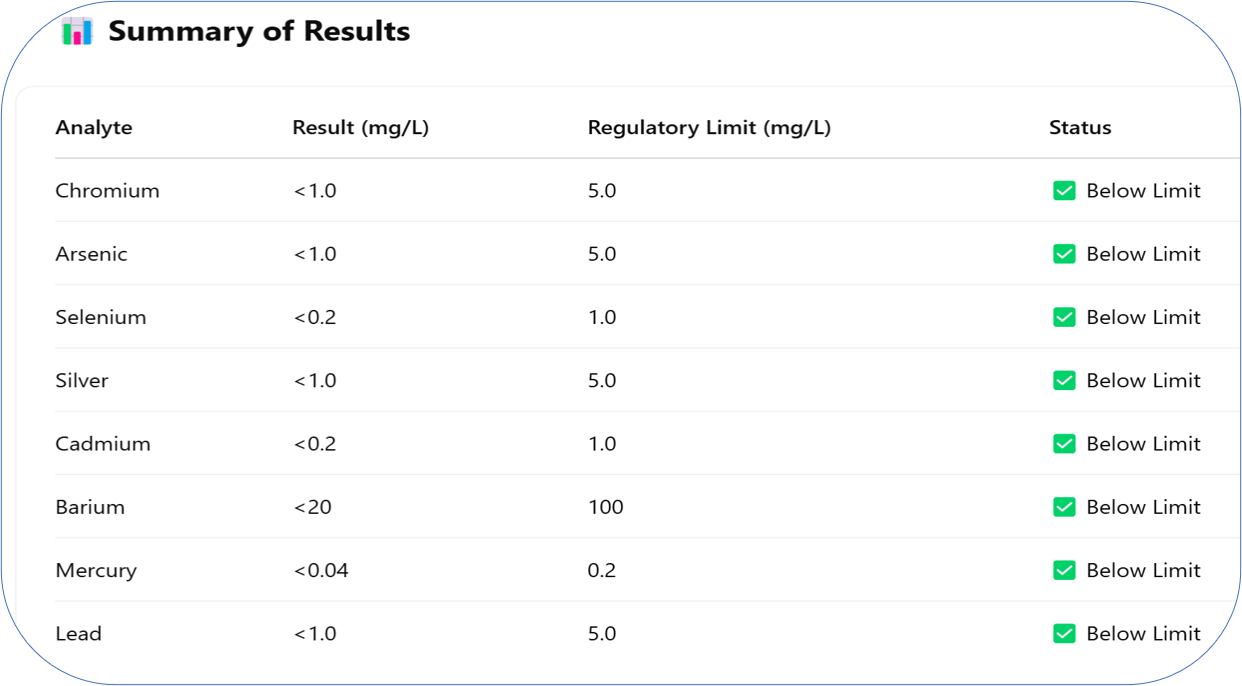
Non-Hazardous Classification
All leached metal concentrations are below the U.S. EPA regulatory limits under 40 CFR 261.24. The Ashcrete sample is not classified as hazardous waste.
Immobilization of Toxic Elements
Toxic metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury are chemically stabilized and not leaching, indicating successful encapsulation within the ashcrete matrix.
Transformation of Ash
This result supports the conclusion that MSWI ash, once incorporated into ashcrete, is chemically transformed and no longer behaves as waste ash.
EPA-Standard Procedure
The test followed U.S. EPA-approved methods (TCLP 1311 and 6020), making the results reliable for regulatory and compliance use globally.
Quality Control Validated
QC data confirms accurate measurements, with most recovery values between 89% and 120%, within accepted limits for analytical precision.
Scientific Validation Conclusion
This TCLP test provides scientific evidence that ashcrete is a safe, stable, and non-leaching material.
It validates that MSWI ash, once treated and incorporated, is transformed into a permanently bound construction material that poses no leaching risk and meets international environmental safety standards.




